Understanding the Richness of Machiguenga Culture and Traditions
Exploring the Machiguenga culture offers us a fascinating insight into a vibrant community deeply woven into the fabric of the Amazon rainforest. With unique traditions, spiritual beliefs, and a strong bond to nature, the Machiguenga culture not only showcases their incredible heritage but also emphasizes the vital connection between humanity and the environment. Let’s embark on a journey to understand the core elements that define this extraordinary indigenous community.
Origins of the Machiguenga People
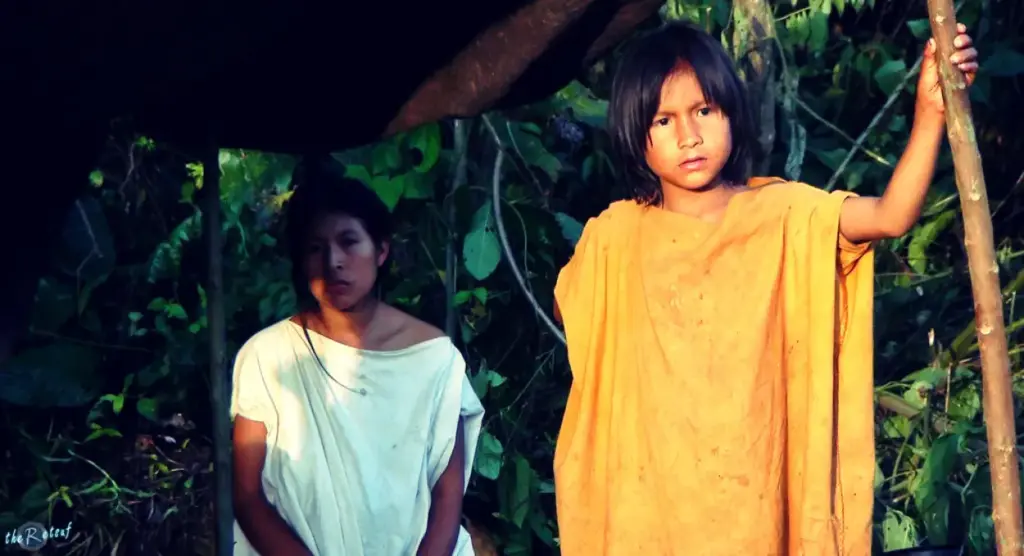

The Machiguenga people have a rich and storied history that dates back centuries in the vast Amazon. Belonging to the Panoan-speaking family, these indigenous people have developed a profound understanding of their surroundings. Their unique origins are shared through captivating myths, often narrated within their communities, reflecting a deep respect for nature and a connection to their ancestors.
Most intriguingly, the Machiguenga believe they are protectors of the rainforest, which serves not only as their home but also as a source of identity and life. The oral traditions of the Machiguenga act as a bridge between past generations and the present, encapsulating values that have stood the test of time. This intergenerational transmission of knowledge is pivotal in maintaining their cultural relevance even in a rapidly changing world.
Spiritual Beliefs and Practices
The spirituality of the Machiguenga is deeply interwoven with their understanding of the natural world. They embrace animism—the belief that all natural elements, from rivers to plants, embody spirits that deserve respect and gratitude. This belief system shapes their daily actions, and their rituals are designed to honor these spirits, ensuring a balanced coexistence with nature.

One fascinating aspect of Machiguenga spirituality is the use of ayahuasca, a sacred brew made from Amazonian plants. This mystical potion is utilized in healing ceremonies, aiming to connect individuals with the spirit world. Participants often describe these experiences as transformative, enabling them to gain profound insight and guidance. Through these rituals, the Machiguenga sustain their cultural identity and reinforce their community bonds.
Traditional Roles Within the Community
In Machiguenga society, traditional roles are intricately defined and influenced by age and gender. Women play a vital part in nurturing the community, embracing tasks such as cooking, gathering food, and sharing stories that preserve cultural knowledge. Their roles emphasize the importance of education in cultural transmission; the stories recounted are instrumental in shaping the identity of the younger generation.
Conversely, men are often tasked with hunting, fishing, and agricultural activities. These roles are not only about sustaining the household but are crucial for teaching skills to future generations. The collaboration between genders fortifies community ties, promoting teamwork that ensures the collective well-being of their society. Interestingly, there is a modern evolution in these roles as women increasingly join leadership positions within their communities, creating a more balanced dynamic.
Language and Communication
The Machiguenga language, a unique aspect of their identity, is pivotal for the preservation of their traditions and stories. As a part of the Pano language family, it features diverse dialects that enrich communication within different communities. The subtle nuances of their language serve as a vessel for expressing cultural values, beliefs, and social norms.
Unfortunately, modern influences pose a threat to their linguistic heritage. However, measures are being taken to document their language and teach younger generations, ensuring its survival. The Machiguenga people view the preservation of their language not just as a means of communication but as a vital component of their cultural identity in a rapidly globalizing world.
Connection to Nature and Sustainability
Central to the Machiguenga culture is a profound connection to nature that permeates every aspect of their existence. This relationship isn’t merely economic; it embodies a spiritual philosophy that underscores their respect for the environment. The rainforest is considered a living entity that provides for and protects the Machiguenga people, making sustainable practices essential for their survival.
The Machiguenga utilize swidden agriculture, a traditional farming method that involves rotating small plots of land to allow for regeneration. This agricultural practice exemplifies their intricate understanding of sustainability, ultimately fostering an ecosystem that supports their dietary and cultural needs. Additionally, their mindful hunting and fishing practices reflect an acute awareness of ecological balance, reinforcing their role as stewards of the Amazon.
Artistic Expressions
Art is a vibrant expression of the Machiguenga culture, serving as a potent means of identity and storytelling. Traditional arts, such as weaving and pottery, often carry profound symbolic meanings. Woven textiles typically feature intricate designs that reflect elements of nature, showcasing the Machiguenga’s appreciation for their environment as well as their artistic skills.
Body art and decorations are also significant aspects of their artistic expression, particularly during ceremonies and celebrations. These body adornments not only enhance their aesthetics but also convey deeper messages about social status and community belonging. Through their art, the Machiguenga articulate their cultural identity, connecting their past with the present while playing a crucial role in cultural continuity.
Modern Challenges and Resilience
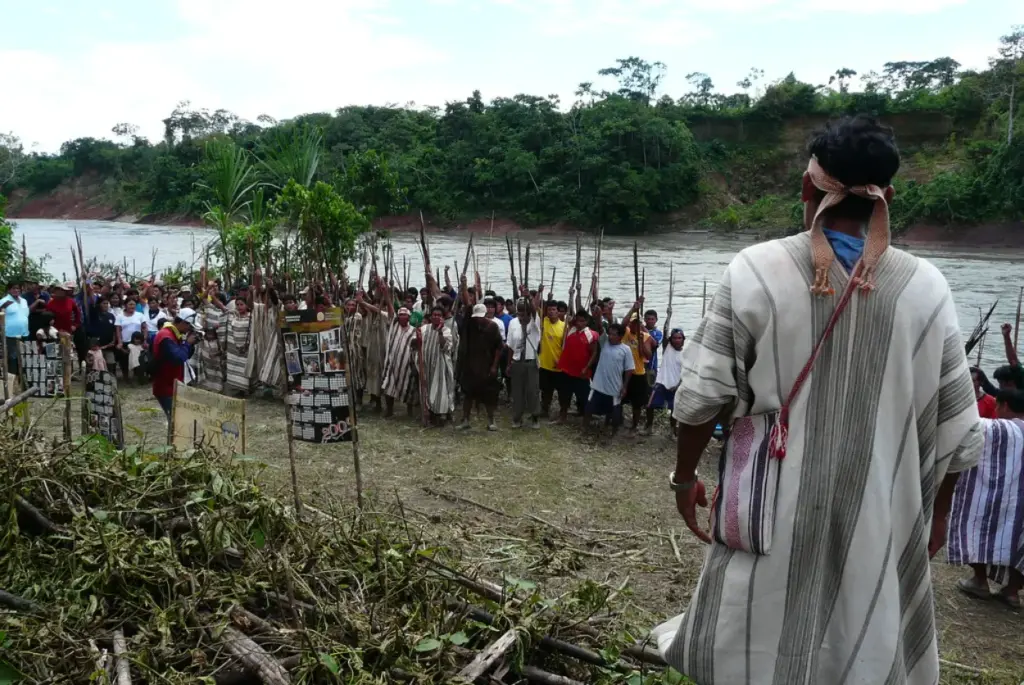
Despite the vibrant traditions and rich heritage, the Machiguenga people face pressing modern challenges. Logging and agricultural encroachment threaten their ancestral lands and, subsequently, their way of life. As these external pressures accumulate, the community must navigate the complex landscape of environmental and cultural preservation. Their ongoing struggle underscores the importance of recognizing and fighting for their rights.
Additionally, climate change poses significant risks to their livelihoods, raising concerns over food security and health. Nevertheless, the resilience of the Machiguenga shines through as they advocate for their community, employing activism and community organization to safeguard their cultural identity. Their determination demonstrates the strength of their heritage, and their ability to adapt speaks to the enduring spirit of the Amazon’s original inhabitants.
Future Directions and Cultural Revival
As awareness grows surrounding the preservation of indigenous cultures, there is a renewed interest in promoting the Machiguenga culture. Educational initiatives aimed at revitalizing traditional practices are gaining momentum, providing opportunities for younger generations to learn essential skills and cultural narratives. This focus on education is vital in ensuring that the rich history of the Machiguenga endures into the future.
Creative collaborations between the Machiguenga community and external entities emphasize cultural preservation and sustainability. Modern society’s acknowledgment of indigenous knowledge systems has the potential to contribute significantly to global discussions about environmental stewardship. The ongoing journey of the Machiguenga culture exemplifies adaptability in the face of change while steadfastly honoring their roots, serving as a powerful testament to the resilience of the Amazon’s first inhabitants.
Conclusion
Wandering through the intricate tapestry of Machiguenga culture allows us to revel in a world rich with spirituality, tradition, and a profound ancestral legacy. Their practices and beliefs illustrate a vibrant community in sync with nature, embodying a unique identity that continues to thrive amidst the challenges of modernity. The Machiguenga people serve as a living reminder of the importance of cultural preservation, sustainability, and the strength that arises from a deep-rooted connection to heritage. By supporting and learning about the Machiguenga culture, we contribute to our understanding of humanity’s diverse tapestry and the crucial role every culture plays in shaping a sustainable future.