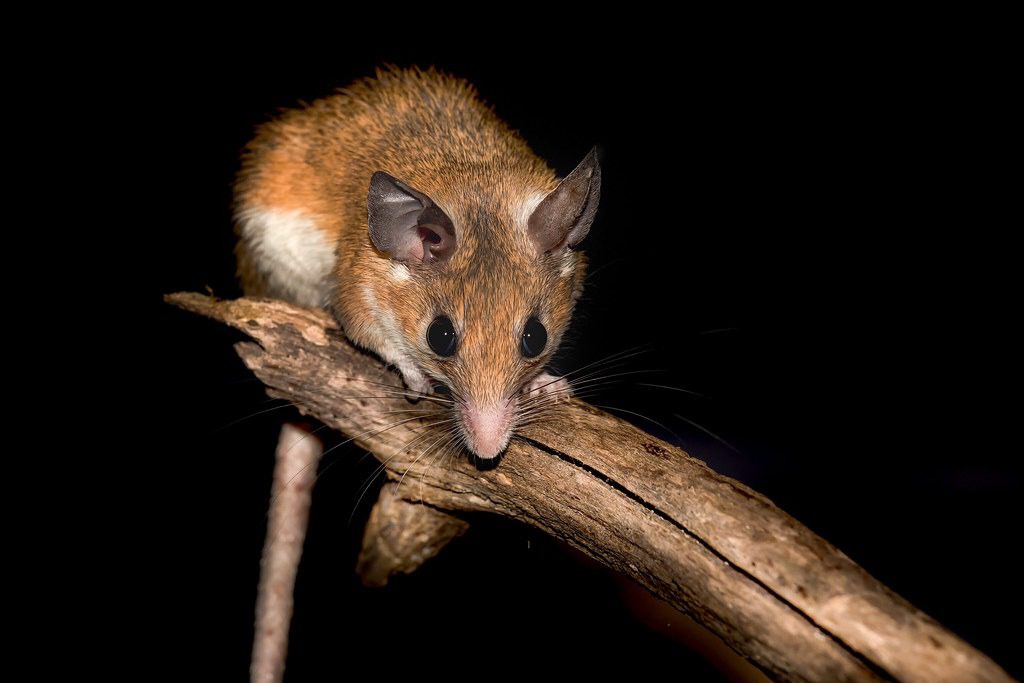
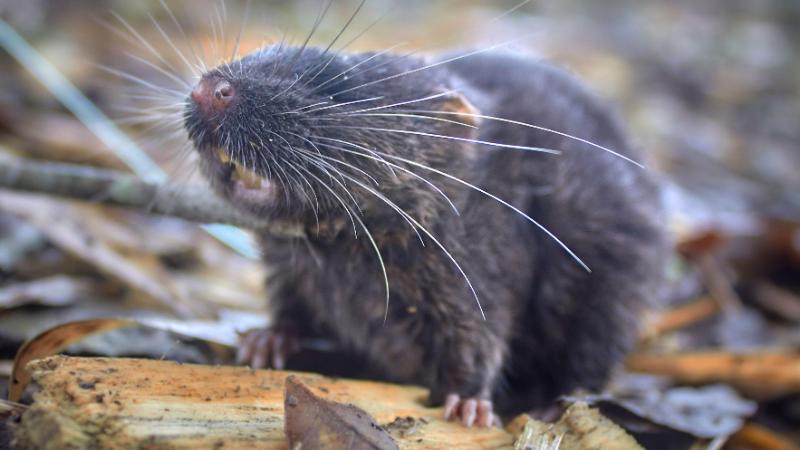
Deep within the lush rainforests of the Amazon, a fascinating creature has emerged from the shadows—one that defies the common characteristics we associate with mice. The Amphibious Mouse, discovered in Peru, is not your average rodent. With webbed feet, a partially aquatic lifestyle, and an elusive nature, this small mammal is revolutionizing our understanding of what rodents can do.

Amphibious Mouse: An Introduction
The amphibious mouse is a newly documented species of rodent that exhibits a rare ability to live both on land and in water. It was discovered in the Amazon basin, where its unique adaptations suggest it may be highly specialized for aquatic life. Unlike typical terrestrial rodents, this mouse shows traits more commonly found in semi-aquatic mammals like otters and beavers.
Its semi-aquatic behavior and physical features have earned it a place among a growing list of amphibious rodents, showcasing evolutionary ingenuity at work in the rainforests of South America.
Amphibious Mouse Discovery
The official amphibious mouse discovery occurred during a field expedition led by scientists in the Manú Biosphere Reserve in Peru, a biodiversity hotspot in the Amazon rainforest. This area is known for its remarkable range of flora and fauna, making it a prime location for new species identification.
Researchers were initially surprised by the mouse’s wet fur and webbed hind limbs, as these features are extremely rare among South American rodents. DNA samples and close examination confirmed that this was indeed a previously undocumented species, triggering excitement in the global scientific community.
Amphibious Mouse Discovered in Peru
The significance of the amphibious mouse discovered in Peru lies in its evolutionary implications. Peru’s Amazon region is often seen as a cradle of biodiversity, and this find supports the idea that the ecosystem may still hold many undiscovered mammalian species.
- Location of discovery: Manú National Park, southeastern Peru
- Elevation: Found between 1,000–2,000 meters above sea level
- Environment: Close to fast-moving streams and humid, forested areas
Scientists believe that the rodent may be endemic to the region, adapted specifically to the microhabitats formed around the park’s rich waterways.
Amphibious Mouse in the Amazon
The amphibious mouse Amazon population is likely limited in range due to the specific habitat it requires. The rainforest provides dense vegetation, abundant insect prey, and a complex network of freshwater systems that the mouse uses for both hunting and shelter.
Its discovery has renewed interest in the Amazon’s lesser-known small mammals, often overlooked due to their elusive behavior and remote habitats.
- Amazonian water systems provide the perfect refuge for the mouse’s aquatic behavior.
- Predator avoidance: Waterways allow escape from ground-dwelling predators.
- Feeding grounds: Aquatic insects and larvae likely form part of its diet.
Amphibious Mouse with Webbed Feet
One of the most unique features of this animal is that it’s an amphibious mouse with webbed feet. This adaptation is uncommon in rodents and allows the animal to swim with agility in fast-moving water.
Physical traits of the webbed feet include:
- Elongated toes with skin stretching between them
- More prominent on the hind limbs than the front
- Provide propulsion in swimming
- May help with grip on slick, wet surfaces
These features suggest a strong evolutionary response to aquatic challenges, akin to adaptations seen in other water-loving species such as water shrews and even some bats.
Amphibious Rodents: An Emerging Class
While rodents are typically known for living in burrows, trees, or urban settings, the rise in interest around amphibious rodents has highlighted several lesser-known species with semi-aquatic capabilities.
Some well-documented amphibious rodents include:
- Capybaras: The world’s largest rodent, fully aquatic
- Beavers: Known for building dams and aquatic habitats
- Water voles: Small rodents found across Europe and Asia
The amphibious mouse from Peru adds to this list, showing that the adaptive potential of rodents may be far more diverse than previously believed.
Adaptations for Aquatic Life
What allows this tiny rodent to thrive both on land and in water? Its adaptations are both behavioral and physical, making it an excellent case study in convergent evolution.
Physical Adaptations
- Webbed hind feet: For powerful swimming
- Water-repellent fur: Keeps the body dry and regulates temperature
- Nostrils placed higher on the snout: Allows partial submersion while breathing
- Streamlined body: Slightly elongated for more efficient movement in water
Behavioral Adaptations
- Nocturnal activity: Helps avoid predators and human interaction
- Burrowing near water: For quick escape routes and easy access to food
- Aquatic hunting patterns: Possibly targets aquatic insects, larvae, or amphibian eggs
What Is Unusual About the Amphibious Mouse?
Several aspects make this rodent truly unusual:
- Rodents rarely exhibit aquatic traits, making this a biological anomaly.
- It was discovered in a relatively well-studied region, suggesting many more unknown species may still be found in the Amazon.
- It resembles a shrew or bat more than a traditional mouse, blurring taxonomic boundaries.
This rodent challenges scientists’ assumptions about rodent evolution and pushes the boundary of mammalian adaptability in extreme environments.
Interesting Facts About the Amphibious Mouse
Here are some lesser-known but fascinating facts about this water-loving rodent:
- 🐾 It is believed to swim using a “dog-paddle” motion, similar to that of small dogs.
- 🌊 Its diet may include aquatic invertebrates, such as water beetles and mosquito larvae.
- 🦠 The mouse’s fur has been found to be resistant to fungal growth, an adaptation to constant moisture.
- 🐁 Its skull structure includes a wider zygomatic arch, possibly linked to enhanced jaw muscles for crunching hard-shelled prey.
- 🌍 It may be part of a new genus, currently being reviewed for classification.
Amphibious Mouse Ecology and Role in the Ecosystem
The amphibious mouse is believed to play a niche ecological role, balancing terrestrial and aquatic food chains.
- As a predator: Likely consumes both land and aquatic insects, helping to control populations.
- As prey: Could serve as food for birds of prey, snakes, and larger fish.
- As a seed disperser: Rodents often help spread seeds, contributing to forest regeneration.
The discovery of such a unique ecological player in the Amazon highlights the interconnectedness of land and aquatic ecosystems.
The Importance of the Discovery
This find is more than a biological curiosity—it has broader implications for:
- Conservation: Highlighting the importance of protecting small, lesser-known species
- Biodiversity studies: Supporting the theory that tropical ecosystems remain vastly under-documented
- Evolutionary biology: Offering a new perspective on how species diversify and adapt
The amphibious mouse could become a symbol for the undiscovered biodiversity still hidden within the world’s rainforests.
Conservation Status and Future Research
As a newly discovered species, the amphibious mouse’s conservation status has not yet been formally assessed. However, its limited range and specialized habitat likely make it vulnerable to:
- Deforestation
- Water pollution
- Climate change
- Habitat fragmentation
Future research directions include:
- Genetic sequencing to determine its relation to other rodent families
- Detailed dietary studies to understand its role in the food chain
- Behavioral observation in controlled environments
How Scientists Found the Amphibious Mouse
The discovery began with field biologists noticing tracks and droppings near stream banks that didn’t match known species. After setting up night-vision cameras and live traps, they captured specimens that showed characteristics previously unseen in regional rodents.
Tissue samples, skull morphology analysis, and behavioral observation confirmed the uniqueness of the species, which is now pending formal classification in scientific literature.
Broader Implications for Amphibian and Rodent Studies
The discovery of the amphibious mouse has prompted a reevaluation of how scientists view both rodent evolution and amphibious behavior in mammals. It suggests that:
- Convergent evolution may be more common than previously thought
- Small mammals are capable of highly specialized adaptations
- Many habitats, even well-studied ones like the Amazon, hold biological surprises
Final Thoughts: Why the Amphibious Mouse Matters
The story of the amphibious mouse is a powerful reminder of how much remains to be learned about our planet. In a single small rodent, we find:
- Evolutionary innovation
- Ecological versatility
- Scientific surprise
As deforestation and habitat loss continue to threaten the Amazon, the need to protect its unexplored regions grows ever more urgent. The amphibious mouse is not just a scientific wonder—it’s a symbol of the wild, unexplored potential that still exists in the natural world.