The Açaí Palm is more than just a tree — it’s a vital source of food, income, and biodiversity in the Amazon rainforest. Known scientifically as Euterpe oleracea, this tall and graceful palm produces the beloved açaí berry, a small fruit that has captured the world’s attention for its rich taste and nutritional power.

From its role in Amazonian culture to its booming popularity in modern superfood diets, the Açaí Palm is a botanical treasure that continues to surprise us with its resilience, benefits, and ecological importance. Let’s explore this fascinating species from root to berry! 🍇
🌿 What is the Açaí Palm?
Origins and Natural Habitat
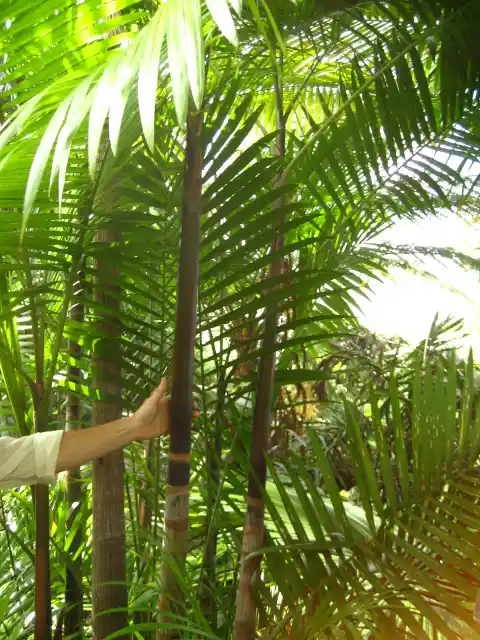
Native to the floodplains and swampy areas of the Amazon Basin, the Açaí Palm thrives in wet, tropical environments. You’ll find it growing in clusters, with up to 20 slender trunks rising from a single root system, reaching heights of 15 to 25 meters. Its natural habitat includes Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, and parts of Peru.

The palm plays a crucial ecological role in stabilizing riverbanks and supporting forest biodiversity. Its towering leaves provide shelter for birds and insects, while its fruits feed a range of wildlife — from monkeys to toucans.
Botanical Features
The Açaí Palm is a multi-stemmed palm, meaning it doesn’t just have a single trunk but grows in dense clusters. Its long, feather-shaped fronds can stretch up to three meters, creating elegant canopies. Each trunk can produce fruit, often twice a year, making it highly productive and desirable for harvesting.
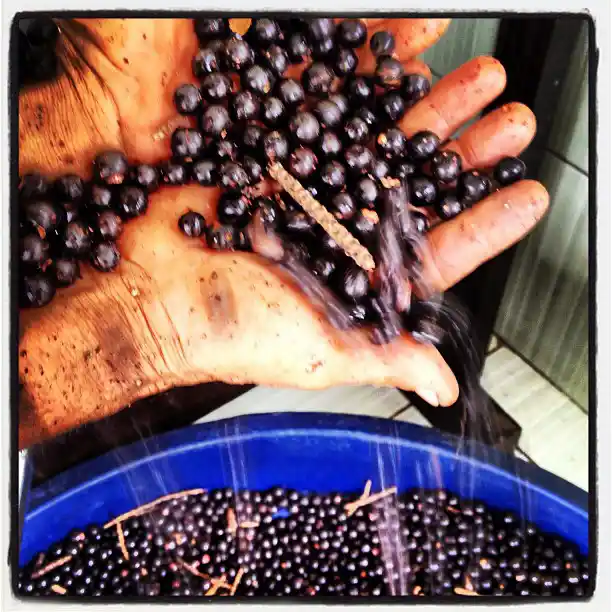
The fruit itself is small — about the size of a blueberry — with dark purple skin and a large seed inside. Though the edible portion is small, it’s packed with flavor and nutrients.
🥣 The Famous Açaí Berry: Nutritional Gold
Superfood Benefits
The açaí berry has earned global fame for its dense nutritional profile. It’s rich in:
- Antioxidants (especially anthocyanins)
- Fiber
- Healthy fats (omega-9 and omega-6 fatty acids)
- Calcium, vitamin A, and iron

These properties make it a powerful agent for fighting inflammation, boosting heart health, supporting digestion, and improving skin vitality. Plus, its low sugar content makes it a popular choice for low-carb and keto diets.
Açaí in Modern Diets
Today, açaí is a global sensation, especially in smoothie bowls, juices, and energy snacks. Its deep purple hue and unique, earthy flavor make it not just healthy but also visually stunning — perfect for Instagram and wellness trends!
However, the traditional way of consuming açaí in the Amazon is quite different. Locals often eat it with cassava flour or fish, highlighting its versatility and importance as a staple food rather than a luxury item.
🌱 Cultivation and Harvesting of the Açaí Palm
Growing Conditions and Methods
To grow successfully, the Açaí Palm requires:
- High humidity and warm temperatures (20°C to 30°C)
- Flooded or well-irrigated soils
- Plenty of sunlight and space to spread out its root system
Farmers typically use seeds or offshoots to propagate the palm. It takes around 3 to 5 years for the tree to begin producing fruit, and once it starts, it can be harvested twice a year — usually during the dry season.
Harvesting and Processing
Harvesting açaí is labor-intensive and done by hand. Workers climb the tall trunks using ropes or notched steps, cutting down the fruit clusters carefully. The berries are then soaked and mashed to separate the pulp from the seed — a delicate process requiring fresh fruit due to its short shelf life.
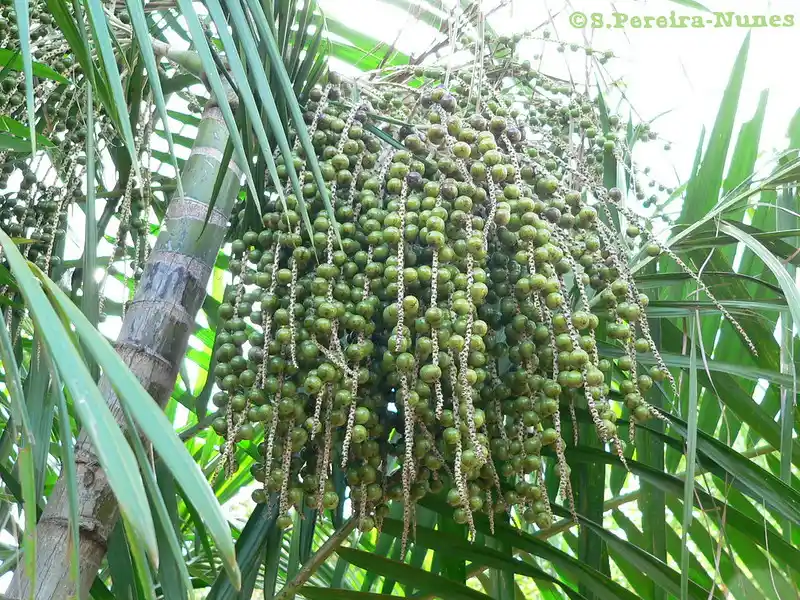

Since the pulp oxidizes quickly, most açaí is frozen or turned into purée near the source to preserve its nutritional value and flavor.
🛖 Cultural Significance in the Amazon
A Staple in Indigenous Diets
Long before it reached supermarket shelves across the globe, the açaí berry was — and remains — a vital food in Amazonian communities. In regions of Brazil, it’s estimated that over 40% of the local diet comes from açaí.
It is consumed daily, especially by riverine populations, who value its energy-boosting and restorative properties. It’s often enjoyed with farinha (toasted cassava flour), making it a nutritious and filling meal in areas where food access can be limited.
Medicinal and Ritual Uses
Beyond nutrition, indigenous groups use parts of the Açaí Palm for traditional medicine. Infusions made from the roots or leaves are used to treat fevers, digestive issues, and even as a natural antiseptic. The palm also holds spiritual significance in certain rituals and ceremonies.
🌎 Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Açaí Harvesting as a Conservation Tool
Unlike deforestation-based agriculture, açaí harvesting encourages forest preservation. Since the palms thrive in natural ecosystems and are harvested without cutting down the trees, they provide a sustainable income source while maintaining the integrity of the rainforest.
This practice is becoming a model for agroforestry — a land-use system that combines agriculture and tree cultivation to protect biodiversity and support local economies.
Threats and Challenges
Despite its eco-friendly image, açaí cultivation isn’t without risks. Overharvesting, monoculture plantations, and increased global demand can put pressure on natural resources. Additionally, climate change and shifts in river flow patterns threaten the fragile ecosystems where Açaí Palms grow.
Proper management and fair-trade practices are essential to ensure long-term sustainability for communities and the forest alike.
🏡 Can You Grow an Açaí Palm at Home?
Indoor and Outdoor Cultivation Tips
If you live in a warm, humid climate (USDA zones 10–12), you can grow Açaí Palms in your garden! These palms love full sun but can tolerate partial shade. They need lots of water — mimicking the swampy Amazon conditions — so regular irrigation is key.
In cooler climates, Açaí Palms can be grown indoors or in greenhouses, though they may not produce fruit. Their elegant, arching leaves make them a beautiful ornamental plant nonetheless. Choose large containers and provide rich, well-draining soil to support healthy growth.
Fertilizing and Maintenance
Feed your palm with a balanced, slow-release fertilizer every 2–3 months. Keep the soil consistently moist but avoid waterlogging. Prune dead fronds as needed and watch for pests like spider mites or scale insects, especially in dry indoor environments.
With the right care, your Açaí Palm can become a striking addition to your plant collection — and maybe even a conversation piece about rainforest conservation!
🧃 Açaí in Modern Markets and Products
Açaí in Global Health Trends
The açaí bowl trend continues to dominate cafes, health stores, and social media feeds. Blended with bananas, granola, honey, and other fruits, the açaí bowl is celebrated as a delicious and energizing breakfast or snack.
You’ll also find açaí in:
- Supplements and capsules
- Energy bars and snacks
- Skincare and beauty products
- Cold-pressed juices and smoothies
Current Innovations and Surprising Uses
Beyond food, innovators are exploring new ways to use açaí byproducts. The seeds — once discarded — are now being used to create biodegradable plastics, jewelry, and even activated charcoal for water filtration and beauty products.
This growing trend of upcycling showcases how the Açaí Palm can support not only nutrition but also sustainable design and industry solutions.
📈 Economic Importance and Fair Trade
Jobs and Local Economies
The açaí industry supports tens of thousands of families across the Amazon. From harvesters to processors and exporters, the value chain is a vital economic engine for many remote communities. In regions of Pará, Brazil, açaí has surpassed beef as the top agricultural product!
Efforts to increase transparency and fairness in the supply chain are helping to protect workers’ rights and improve incomes for small-scale producers. When you buy fair-trade certified açaí, you’re helping support these initiatives.
Women in the Açaí Economy
Women play a central role in the processing and preparation of açaí, especially in traditional communities. Empowering women through cooperatives and education is an increasingly important part of the açaí story — contributing to gender equity and long-term sustainability.
🌟 Fun and Fascinating Açaí Facts
- 🔥 Açaí berries must be processed within 24 hours of harvest or they spoil — that’s why most açaí outside of South America is frozen!
- 🌊 Açaí palms help control flooding by stabilizing soil and filtering water naturally.
- 🌌 The deep purple color of açaí comes from anthocyanins, the same pigments that give blueberries and red wine their antioxidant power.
- 🍷 In some Amazonian communities, açaí juice is fermented into a kind of wine — used in social and ceremonial gatherings.
- 🪵 Açaí palm wood is used in house construction, fencing, and crafts due to its durability and flexibility.
🌱 Final Thoughts: Why the Açaí Palm Deserves the Spotlight
The Açaí Palm is more than a passing food trend. It’s a living symbol of the Amazon’s resilience, diversity, and natural abundance. From its nutrient-rich berries to its role in preserving ecosystems and empowering communities, this extraordinary tree offers far more than meets the eye.
So the next time you enjoy an açaí bowl, remember — you’re tasting a piece of the rainforest, grown by nature and sustained by tradition. 🌿💜
🌿 Want to Go Deeper?
Consider supporting sustainable açaí farming, visiting agroforestry projects, or learning more about Amazonian culture. Every bite counts toward a better future for the forest and its people.